$09 Vehicle Information Request
MODE $09 reports the following vehicle information requests if the system supports it. Before 2005, OBD II systems were not required to support this MODE, yet many did. Starting in 2005, all systems were required to report the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN), Calibration Identification (CAL ID), and Calibration Verification Number (CVN).
In 2008, CAN "C" equipped systems added one more thing to the MODE: In-Use Monitor Performance Tracking (IUPMT).
This section about OBD II Vehicle Information will cover the following:
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
- Calibration Identification (CAL ID)
- Calibration Verification Number (CVN)
- In-Ude Performance Monitor Tracking (IUMPT)
Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is a unique, 17-digit, alphanumeric number assigned by the manufacturer to every vehicle built. The VIN is commonly used for ownership and registration to identify every vehicle uniquely. As such, the VIN is also used during an I/M inspection to determine the exact vehicle being tested. Current Inspection & Maintenance (I/M) programs require the inspector to enter the VIN at the time of inspection by manually typing it in or, in some cases, using a bar code reader to “scan” it in. However, errors can and do occur when the VIN is manually entered.
To reduce the number of errors related to VIN entry, facilitate VIN access, and further deter fraud during I/M inspections, the regulations require the VIN to be stored in the vehicle’s onboard computer and accessible electronically via a generic scan tool. This is required on all 2005 and newer model-year vehicles. While this does not eliminate the possibility of a technician performing a fraudulent inspection, it would make it significantly more difficult.
The VIN is also used to order replacement parts and to identify recalls and warranty issues.
Calibration Verification Number (CVN)
OBD II diagnostics comprises software routines and calibrated limits and values to determine if a component or system is malfunctioning. Manufacturers often release updates to the software in the onboard computer to add new features and improvements or correct errors or “bugs” in the system. To determine if the right software had been installed, amendments were adopted in 1996 that required manufacturers to phase in the reporting of two additional items:
- Calibration Identification Number (CAL ID) identifies the version of software installed in the vehicle.
- Calibration Verification Number (CVN) is used for all OBDII vehicles. It assures that emissions software has not been tampered with. If the vehicle is not modified, the ECM/TCM Part number will have a corresponding CVN. MODE $09 will report the CVN for the Engine and Transmission Controller. ECM/TCM calculates the CVN at each key-on cycle. After a Reflash, it can take a few minutes to calculate a new CVN.
The CVN is used to verify that the emission controller software has not been modified using an aftermarket “Tuner.” The aftermarket “Tuner” may claim the ability to reset to factory settings, but in most cases, it CANNOT reset the CVN to the factory setting. Once incremented, it cannot go back; it might even be missing or not reporting after this procedure!
The CAL/CVN are used together to identify Modified Software during a state emissions inspection in California. At the vehicle’s first smog inspection, the OIS collects the eVIN, Software Calibration Part Number, and CVN. This information will be used to compare data for future smog inspections. If the eVIN and Software Calibration Part match the database for follow-up inspections, but the CVN has changed, the vehicle could fail the inspection.
If the vehicle was “tuned” before its first inspection, then that information will establish the baseline for future smog inspections for this vehicle. CARB/BAR is getting some of this information directly from the OEMs.
In-Use Monitor PERMORMANCE Tracking (IUMPT)
What is MODE $09 - In-Use Monitor Performance Tracking (IUMPT):
In-Use Monitor Performance Tracking (IUMPT): checks that the vehicle runs its Non-Continuous Monitors at a minimum frequency to identify most emission-related failures. Vehicles identified as not meeting the minimum frequency for running Non-Continuous Monitors will require the OEM to generate a fix like a Reflash or Component Update.
Before attempting to Complete a Readiness Flag, review (IUMPT) to identify the frequency at which a particular Readiness Flag has Completed testing in the past. This information can be used to determine if an individual Readiness Flag will be easy or challenging to Flip to Complete.
IUMPT can also indicate the vehicle's driving experiences, the type of vehicle it is, like a Hybrid or other Start/Stop system, or if ECM reprogramming has recently been performed.
IUMPT results include the word Completions, referred to as the Numerator. It represents the actual Monitoring events where the enable criteria ran long enough that a malfunctioning component or system would have been detected. Whether the Readiness Flag Passes or Fails, the Completions will be incremented (See image below).

IUMPT results include the word Conditions (See image above), referred to as the Denominator. It represents a generic enable criteria establishing a charged Trip against the OEM if met. To meet the Conditions, the vehicle must be driven for 10 minutes, including 5 minutes above 25 mph, and one 30-second idle period. Completions do not indicate how frequently the Readiness Flag has been completed or the chance of Completing a given Readiness Flag (See image below).
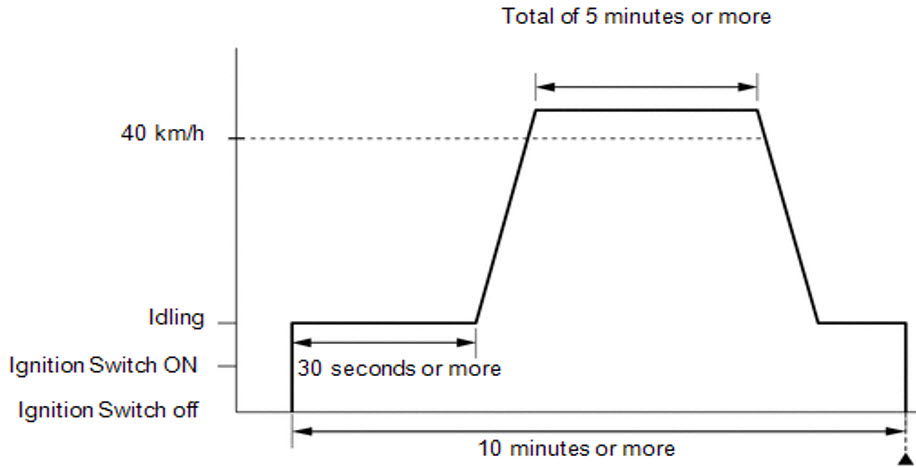
In-Use Monitor Performance Ratio (IUMPR). Knowing the number of Completions (Numerator) and Conditions (Denominator) creates an In-Use Monitor Performance Ratio. The ratio, the Numerator divided by the Denominator, allows tracking of the frequency with each readiness flag's enable criteria run long enough that a malfunctioning component or system would have been detected. A Confirmed or Pending DTC will temporarily suspend the incrementing of Completions and Conditions (See image below).
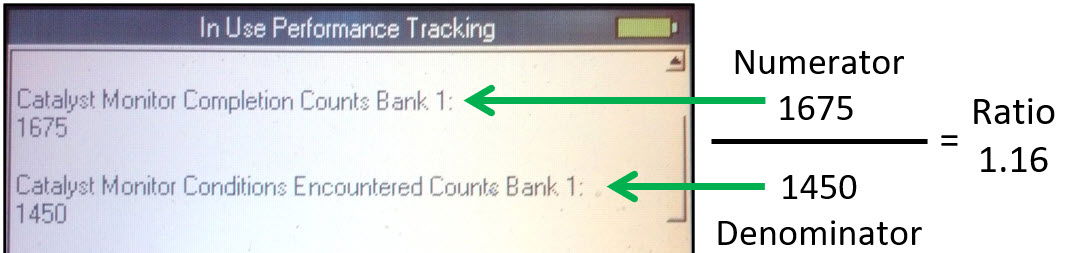
What does the In-Use Monitor Performance Ratio (IUMPR) above indicate? CARB set the minimum acceptable IUMPR at 0.336 for the Catalyst. This vehicle had an IUMPR of 1.16. which is well above the required minimum, so the monitor test(s) related to the Catalyst should have been easy to complete. In this case, the technician confidently quoted a price for running the Catalyst monitor test(s) to prepare the vehicle for a state emissions inspection or to verify a repair.

